In just nine months, Biden’s net ratings have plunged by a stunning 20 percent, which leaves him behind all U.S. postwar presidents except for Trump, many of whose policies his White House has embraced. Today, Biden’s performance divides the nation, just as Trump’s did before him.
True, Biden pledged to end America’s longest war in Afghanistan. That does not spell end to the “forever wars.” It only means shifts of resource allocations to new regions. Last June, Bernie Sanders warned that such policies could "start another Cold War” against China.
The global challenges America faces – climate change, pandemics, nuclear proliferation, massive economic inequality, corruption and authoritarianism – are shared challenges. They cannot be overcome unilaterally, Sanders warned. It is “distressing and dangerous that a fast-growing consensus is emerging in Washington that views the U.S.-Chinese relationship as a zero-sum economic and military struggle.”
But if such policies are misguided, who benefits from the Cold War against China?
Revolving-door politics behind militarized foreign policy
In 2019, Biden’s Asia Tsar Kurt Campbell and National Security Advisor Jake Sullivan touted a new China doctrine of stiff “competition without catastrophe.” As in the ‘50s, the effective objective is to militarize containment policy and minimize U.S. costs by diversifying risks to allies and proxy conflicts into Asia.
The new Cold War promoters like to refer to George Kennan, the architect of U.S. containment against Russia in 1947. Here’s the irony: Kennan himself began to push for dialogue with Moscow already a year later, when he denounced the Truman administration’s “distorted” and “militarized” version of containment – which, he stressed to CNN in 1996, “led to 40 years of unnecessary, fearfully expensive and disoriented process of the Cold War.”
So why the disastrous doctrine? The short answer: It pays off to its promoters.
President Biden’s greatest mistake has been his willingness to let a handful of policy experts, each of whom has deep economic ties with defense contractors, to take over U.S. foreign policy. The credibility of each – Campbell, Sullivan, Secretary of State Antony Blinken, and Secretary of Defense Lloyd Austin – is undermined by conflicts of interests, as U.S. government watchdogs and investigative journalists have recently reported.
The consequent U.S.-Sino tensions were not inevitable. They are manufactured outcomes of the privatization of U.S. foreign policy vis-a-vis campaign finance and revolving-door politics between the White House, the Pentagon and its contractors - as evidenced by the plunge of the bilateral ties.
Bilateral collapse
During the Trump administration, bilateral relations plunged to a historical low. Instead of the hoped-for reset, Biden embraced Trump’s far-right anti-China policies.
High-Level Dialogues. Presidents Trump and Xi met five times in 2017-19, but the dialogue effectively collapsed. In the Biden era, top-level dialogue is limited to a phone call in which Biden aimed to set “guardrails and parameters” so that “stiff competition does not veer into conflict.” But in China, unilateral directives amid an unwarranted Cold War sound like a bully's monologue.
Trade. In bilateral trade, Biden embraced Trump’s protectionism and tariff wars. Both have hit hard American consumers. Similarly, U.S. businesses are frustrated with Biden’s decision to retain Trump’s confrontational China policies. They know that Cold Wars are usually preludes to Hot Wars. In 1930, President Herbert Hoover signed the Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, which worsened the effects of the Great Depression, serving as a prelude to still another world war (Figure 1).
Figure 1 The Trump-Biden Tariffs toward Hot War
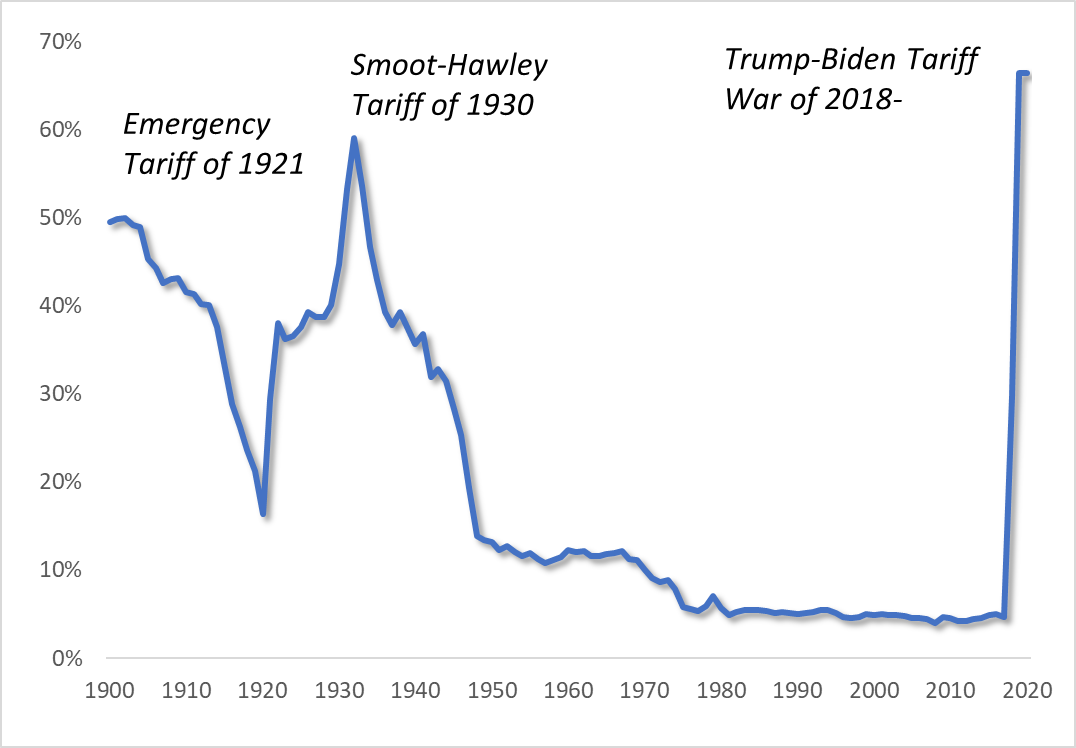
Sources: Chad P. Bown and Douglas A. Irwin 2018.
Investment. In 2016, prior to the Trump era, U.S. foreign investment in China was $15 billion, while Chinese investment in the U.S. soared to more than $50 billion. Today, each figure is closer to $8 billion (Figure 2).
Figure 2 FDI transactions between the U.S. and China, 2000-2020 ($ bn)
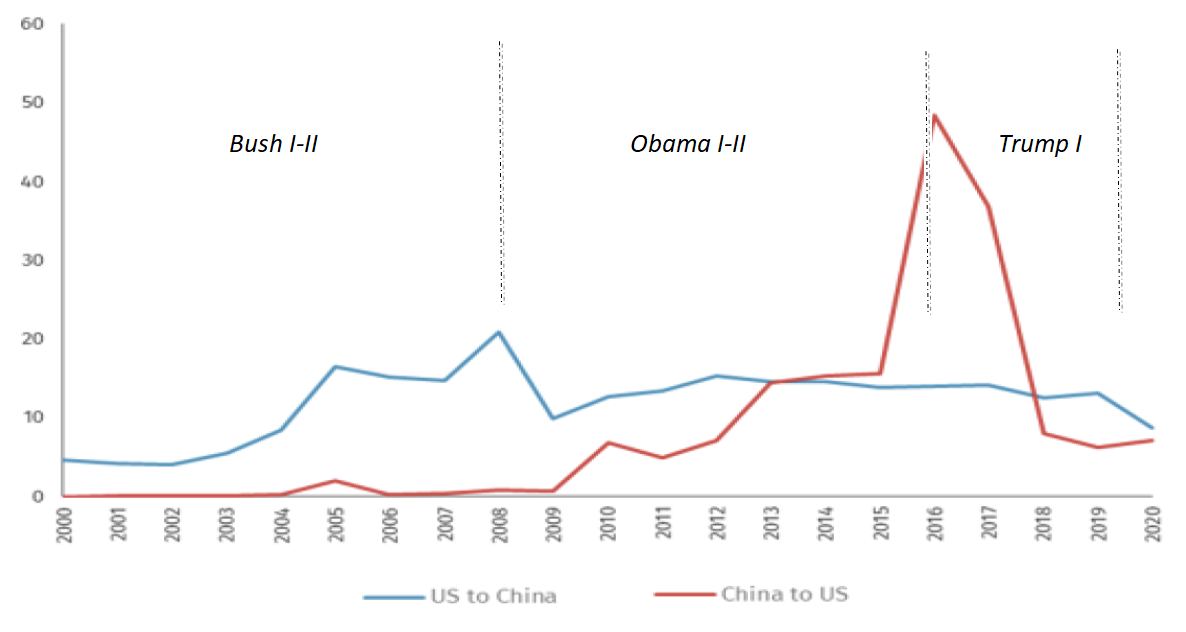
Source: Rhodium Group; Difference Group
Military-to-Military Relations. If a bilateral catastrophe is to be avoided, high-level military ties play a critical role. Yet, in the Trump era, U.S.-China military engagements fell from $30 billion in 2016 by more than two-thirds by 2019, while plunging in 2020. What’s left focuses narrowly on risk reduction.
Climate change. In the Obama era, climate change was the one area of bilateral ties that showed the promise of cooperation. In the Trump-Biden era, that promise is fading, as Biden’s climate diplomat John Kerry discovered recently in Beijing. When Kerry urged China to move its peak emissions target, foreign minister Wang Yi noted that when Washington's grand strategy has targeted China as a “threat and adversary,” it puts all bilateral cooperation at risk.
The current tensions are the net effect of a decade of missed opportunities.
Opposite stances to manage Sino-U.S. ties
In 2013, when Chinese President Xi Jinping met with President Obama at Sunnylands in California, he promoted the idea of a “new type of great-power relations.” When the Pax Britannica was superseded by the Pax Americana, the lingering transition resulted in two world wars. As the size of the Chinese economy is projected to exceed that of the United States by the late 2020s, Xi saw a historical opportunity to avoid misguided conflicts and to focus on economic development that would benefit both major powers.
However, the Obama administration stayed away from the idea, nixed it and replaced it with the shift to “renewed great power competition.” The new doctrine was first affirmed in the Obama administration’s National Military Strategy (Jun 2015). And it was placed at the center of the Trump administration’s National Security Strategy (Dec 2017) and National Defense Strategy (Jan 2018).
Stressing inclusion, dialogue and multilateralism in the global economy, China advocated "new type of great power relations," which Washington rejected. Emphasizing the quest for full spectrum military supremacy, the U.S. promoted increasing force deployments and large-scale, high-end warfare capabilities against Beijing.
The contrast between the two stances could not be greater (Table 1).
Sleepwalking into catastrophe
Since 1945, Asia has seen some of the most successful economic modernization efforts . But after a decade of the U.S.’s policy to “Pivot to Asia,” arms races and nuclear threats risk undermining the Asian Century.
According to the new trilateral security pact (AUKUS) between the U.S., the UK and Australia, Washington and London will help Canberra develop and deploy nuclear-powered submarines. The $66 billion deal effectively killed Australia’s $90 billion conventional sub deal with France, angering French officials. Stunningly, U.S. and Australian officials had been in secret talks for months over the plan that was hatched more than a year ago by the far-right Trump administration. Yet, it was both embraced and accelerated by the Biden White House.
To conclude, neither the White House nor the Pentagon seem to be effective in setting the pace for the U.S.-China relationship. As the international community focuses more heavily on security and defense, shifts of power towards those groups are inevitable.
