Robin Rivaton, CEO of Stonal, an AI sherpa to MEDEF
Feb 13, 2026
When Western politicians and business leaders discuss China’s manufacturing prowess, they typically invoke images of colossal steel mills flooding global markets, dark factories run by robots, and state-owned champions sustained by subsidies. This supports the view that tariffs and anti-subsidy measures can erode China’s industrial dominance. But while this logic may be comforting, it is wrong.

Dan Wang, China Director, Eurasia Group
Jan 05, 2026
China has deliberately kept the yuan stable in recent years, prioritizing currency credibility and controlled internationalization over export-driven devaluation, as a weaker currency now risks trade tensions, regional instability, and undermining long-term strategic goals. Rather than challenging the dollar outright, Beijing is pursuing a state-led, sanctions-resilient financial system and gradually re-anchoring its exchange rate away from a tight dollar peg toward a more multipolar framework.

Zhu Zhongbo, Director, Department for International and Strategy Studies, China Institute of International Studies
Dec 18, 2025
The national development strategy advocates for a multipolar world and seeks to implement global initiatives on development, security, civilization and governance. It opposes hegemony, defends justice and promotes a world of lasting peace, prosperity, openness and sustainability.

Ludovic Subran, Chief Investment Officer and Chief Economist at Allianz
Dec 09, 2025
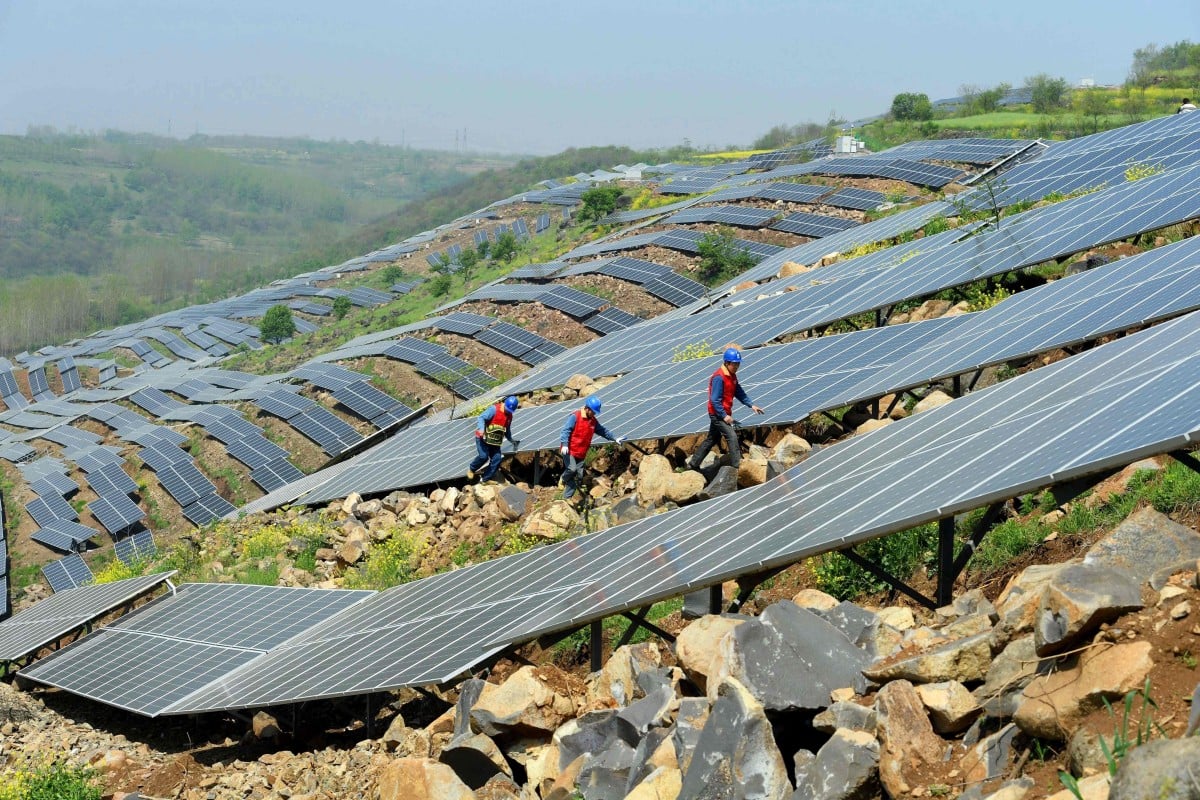
Another great transformation is underway in China. The world’s factory is fast becoming its first electro-state, with an economy increasingly built on clean energy, AI, advanced manufacturing, and control of key strategic materials. This new model is full of promise, though it faces major challenges.

Zhou Xiaoming, Former Deputy Permanent Representative of China’s Mission to the UN Office in Geneva
Nov 21, 2025
High import duties on Chinese goods have become the new normal for the United States. While there’s lots of talk about renewed stability with China after the presidents met in South Korea, but the world’s two largest economies appear to be learning how to live apart.

Warwick Powell, Adjunct Professor at Queensland University of Technology
Nov 10, 2025
In the geopolitical theater of 2025, the United States’ trade posture toward China exemplifies a pattern of escalating threats that yield diminishing strategic returns.

Yu Xiang, Senior Fellow, China Construction Bank Research Institute
Oct 28, 2025
Under China’s 15th Five-Year Plan, the coming period will be crucial for consolidating foundations and achieving socialist modernization. The country aims to leverage four key advantages: its institutional strengths, its vast domestic market, its complete industrial system and its abundant human resources.

He Weiwen, Senior Fellow, Center for China and Globalization, CCG
Oct 09, 2025
China’s decision to forgo special rights in the WTO shows that it takes its great power responsibility seriously. It wants to advance trade cooperation with developed economies and with Global South. A trade upturn with the United States in 2026 is much anticipated.

Zhang Monan, Deputy Director of Institute of American and European Studies, CCIEE
Oct 08, 2025
Beijing’s announcement regarding future World Trade Organization negotiations is strategic. It represents both a willingness to promote WTO reform and an institutional adjustment to support high-quality domestic development and opening-up to the world.

Brian Wong, Assistant Professor in Philosophy and Fellow at Centre on Contemporary China and the World, HKU and Rhodes Scholar
Sep 19, 2025
China’s economic struggles have implications for its trading partners across the globe, notably in Europe. What can Beijing’s fight against ‘involution’ tell the world about its future trading prospects?
Back to Top

- China-US Focus builds trust and understanding between the U.S. and China through open dialogue among thought leaders.
- Our Offerings
- Topics
- Videos
- Podcasts
- Columnists
- Research Reports
- Focus Digest
- Stay Connected
-
Thanks for signing up!
- Get the latest stories from China-US Focus weekly.